California History
Review
Lesson 30
1. What are California’s four regions? (mountains, valleys, ocean, desert)
2. What is the lowest point in California? (Death Valley)
3. How did the first Californians come to California? (land bridge or boat)
4. What was one craft all the Indian tribes made? (baskets)
5. Most of the explorers came from what country? (Spain)
6. What were the ships the explorers traveled in called? (Spanish Galleons)
7. Why did Spain want to establish missions? (To claim land or to teach Indians about God)
8. How many missions were established? (21)
9. What was created to replace the missions by Mexico? (ranchos)
10. What three things did cattle provide? (meat, hides, tallow)
11. What do we call the battle between America and Mexico for possession of California? (Bear Flag Revolt)
12. Where was the first gold found? (American River or Sutter’s Mill)
13. What do we call the people who came looking for gold? (49ers)
14. What does “Eureka” mean? (I found it!)
15. What mammal represents the state of California? (California Grizzly Bear or California Gray Whale)
16. What two ways did people travel to California before the transcontinental railroad was built? (ship, stagecoach)
17. What was the first speedy way for mail to be delivered before the telegraph? (Pony Express)
18. What helps California to grow so many crops? (climate or warm weather)
19. What do we call people who move from one country to another to live? (immigrants)
20. Name one thing that led people to want to live in California. (wealth or weather or farmland)
21. What became known as “Black Gold”? (oil)
22. What two industries grew during World War II? (airplane and ships)
23. What is the largest city in California? (Los Angeles)
24. Who leads the Executive branch in California? (Governor)
25. What is the State Capital of California? (Sacramento)
Our homeschool life is characterized by LEARNING new things, EXPLORING the world around us and DISCOVERING who we are in Christ; aka LEAD. . . "Give me wisdom and knowledge, that I may lead." 2 Chronicles 1:10
Monday, August 13, 2018
California History Lesson 29 (Government)
California History
Government
Lesson 29
Like the United State’s government, California’s state government is divided into three parts. Our government - both federal and state - is set up so no one person or group have too much power. The three branches are kept in balance by the other two.
The Legislative Branch
The United States:
In the national government the Legislative Branch consists of two houses: the House of Representatives and the Senate. The House of Representatives has 435 members. The Senate has 100 members.
United States:
In the national government the Executive Branch consists of the President, Vice President and his cabinet members.
California:
In the California government, this branch is made up of the Governor and state agencies.
The Governor heads the executive branch. He or she is the highest official in the state government. When the Legislative Branch passes a law, the governor either signs it to make it official or vetoes it. The Governor also makes the state’s budget.
Judicial Branch
United States:
In the national government there are three courts - the District Courts, Court of Appeals and the Supreme Court. In the Supreme Court there are 9 Supreme Court judges who are appointed by the President.


2. California Facts and Symbols worksheet (p. 22 A State Theme Unit California The Golden State by Instructional Fair, Inc.)
3. California Poppy
Government
Lesson 29
Like the United State’s government, California’s state government is divided into three parts. Our government - both federal and state - is set up so no one person or group have too much power. The three branches are kept in balance by the other two.
The Legislative Branch
The United States:
In the national government the Legislative Branch consists of two houses: the House of Representatives and the Senate. The House of Representatives has 435 members. The Senate has 100 members.
The job of the Legislative Branch is to make laws, declare war, confirm Presidential appointments and investigate power.
California:
In California we have the Assembly and the Senate. In the Assembly there are 80 members. In the California Senate there are 40 senators.
California Legislators write laws. They also help to decide how the state will spend its money.
Executive Branch
California:
In California we have the Assembly and the Senate. In the Assembly there are 80 members. In the California Senate there are 40 senators.
California Legislators write laws. They also help to decide how the state will spend its money.
Executive Branch
United States:
In the national government the Executive Branch consists of the President, Vice President and his cabinet members.
The job of the President is to sign or veto laws, enforce laws, signs treaties and pardon criminals.
California:
In the California government, this branch is made up of the Governor and state agencies.
The Governor heads the executive branch. He or she is the highest official in the state government. When the Legislative Branch passes a law, the governor either signs it to make it official or vetoes it. The Governor also makes the state’s budget.
Judicial Branch
United States:
In the national government there are three courts - the District Courts, Court of Appeals and the Supreme Court. In the Supreme Court there are 9 Supreme Court judges who are appointed by the President.
Their job is to interpret the laws.
California:
In the California government the Judicial Branch is made up of trial courts and the California Supreme Court. The Supreme Court is made up of 7 judges.
The job of the California Judicial Branch is to decide if the the laws agree with the California Constitution.
Activities:
California:
In the California government the Judicial Branch is made up of trial courts and the California Supreme Court. The Supreme Court is made up of 7 judges.
The job of the California Judicial Branch is to decide if the the laws agree with the California Constitution.
Activities:
1. Fill in the chart
2. California Facts and Symbols worksheet (p. 22 A State Theme Unit California The Golden State by Instructional Fair, Inc.)
3. California Poppy
| Link |
California History Lesson 28 (New Century)
New Century
Lesson 28
In the 1960’s people fought for Civil Rights - freedoms as citizens - for minorities. A minority is a group of people that is a smaller part of the whole population. Black Americans fought for the things like the right to buy houses and to be hired for jobs. Migrant farm workers fought for fair wages and better working conditions. They created a labor union - a group of workers joined together to protect their own rights.
California’s population grew by more than half a million people in 1999. There are more people living in California than in any other state in the United States. Eight of every ten residents live in cities. The four largest cities are Los Angeles, San Diego, San Jose, and San Francisco. Los Angeles is the largest city.
The majority of immigrants to California come from Asia and Latin America. A new law passed in 1965 allowed many more immigrants to come to the United States. The war in Vietnam in the 1960’s and 1970’s created refugees - people who flee their homeland to find safety or freedom. Many came to California. About one third of all Asian people living in the United States live in California. Refugees from Central America have also found refuge in California. Immigrants have enriched California’s culture with different food, art, music, games and dances.
California is the eighth largest economy in the world. Most jobs are industrial - done by machines. Products are produced for computers, electronic components, missiles and scientific instruments. There are many laboratories for research and testing. The Silicon Valley in Santa Clara county is the world’s leader in the production of high-technology equipment. Computer technology has helped the movie industry by creating special effects. Computers and movies are California’s largest exports - products sold to other countries. Other exports are oil, blue jeans, agricultural products and airplanes. California imports many products from other countries; mostly from countries in Asia. These include cars, cameras and silk fabrics.
Transportation is a growing problem. New freeway systems have been built and many miles of highway added. The BART system in the Bay Area and the Red and Blue Lines in Los Angeles have been created, but most people prefer their automobiles. Ride-sharing is encouraged and carpool lanes help.
The air quality of California is getting worse. The emissions from automobiles and factories creates pollution - the smoke, dirt and gases that make the air unclean and smoggy. California has some of the dirtiest air in the United States. Laws have been passed for cars to be made with a device to trap pollution from engine exhaust. Cars are now designed to burn less gas than the bigger cars of the past.
California has had problems with power In 2001, there were rolling “blackouts”. Too many private power companies and not enough power plants led to this problem. The summer of 2001 was mild, people began conserving energy and six new power plants were opened. By the end of 2001, there was an energy surplus.
The Los Angeles Aqueduct brought water to Los Angeles, but it created dust storms in the Owens Valley where cattle used to graze and crops grew. In 1941, Los Angeles needed water again. The aqueduct was extended to Mono Lake. A shrimp lives in the lake that feeds the birds that nest there. As the water level dropped, the water began getting saltier and the shrimp began to die. This meant the birds had less food. Sometimes meeting the needs of people can cause damage to the soil, water, animals, plants and other parts of nature that make up the environment. Now we think about conservation - the protection of natural resources like water and forests. Less water is taken from Mono Lake to help protect, or conserve, it.
In the 1920’s, golf courses, homes and hotels began to spread across the Coachella Valley. By 1980, the fringe-toed lizard had become an endangered species. That meant they were in danger of disappearing forever. In 1986 scientists, government officials, builders, environmental groups and the people who lived in the valley came up with a plan to divide the valley. Part of the land was kept for the builders and part was set aside for the lizard.
Education has been under attack for not measuring up to the other states. Class sizes are bigger. Buildings are older. There are more non-English speaking students. Many Charter schools have been started. There has been an increase in enrollment in Christian and private schools as well as a growth in homeschooling. California has the largest system of state colleges and universities in the United States.
Several new museums and Art centers have been established. The Getty Center, the Museum of Contemporary Art in San Diego, the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art, the M.H. de Young Memorial Museum, the Asian Art Museum in Golden Gate Park in San Francisco, and the Long Beach Aquarium of the Pacific are some examples.
Activities:
1. Matching Worksheet
California History Lesson 27 (Industry/War Times)
California History
Industry / War Times
Lesson 27
Definition of industry - processing of raw materials and the manufacture of goods in factories.
California has many natural materials that supply many needs.
Oil has been in California since the very first inhabitants. It was used by the Chumash Indians to seal canoes. The Californios used it to make adobe roofs. It became known as “black gold” following the Gold Rush. It is used to make diesel fuel for trains and tractors, then to make gasoline for automobiles The oil industry helped California grow by bringing in more money and people and helping new industries to be developed.
Water is important to California. The Los Angeles Aqueduct brought water from the Owens River to Los Angeles. A giant pipe was built to take water through the Sierra Nevada and Mojave Desert to Los Angeles. Farmers were not happy about losing their water and tried to stop it; but the San Fernando Valley became a major farming region. This allowed Los Angeles to continue to grow because it became a major grower of many foods for the entire United States.
A “harbor” is a protected body of water that is deep enough for ships to dock in. San Francisco and San Diego are natural harbors; but the San Pedro Harbor was man made. Los Angeles had a straight coastline and its waters were not deep enough. In 1899 a harbor began to be dug. It was completed in 1914. Because of this, Los Angeles became a major port which allowed for growth and new industries.
The Folsom Powerhouse was built in 1895. Water from the American River was used to run generators. It allowed electricity to be transmitted 22 miles downstream to Sacramento. This was the farthest electricity had been transmitted at that time.
Industry / War Times
Lesson 27
Definition of industry - processing of raw materials and the manufacture of goods in factories.
California has many natural materials that supply many needs.
Oil has been in California since the very first inhabitants. It was used by the Chumash Indians to seal canoes. The Californios used it to make adobe roofs. It became known as “black gold” following the Gold Rush. It is used to make diesel fuel for trains and tractors, then to make gasoline for automobiles The oil industry helped California grow by bringing in more money and people and helping new industries to be developed.
Water is important to California. The Los Angeles Aqueduct brought water from the Owens River to Los Angeles. A giant pipe was built to take water through the Sierra Nevada and Mojave Desert to Los Angeles. Farmers were not happy about losing their water and tried to stop it; but the San Fernando Valley became a major farming region. This allowed Los Angeles to continue to grow because it became a major grower of many foods for the entire United States.
A “harbor” is a protected body of water that is deep enough for ships to dock in. San Francisco and San Diego are natural harbors; but the San Pedro Harbor was man made. Los Angeles had a straight coastline and its waters were not deep enough. In 1899 a harbor began to be dug. It was completed in 1914. Because of this, Los Angeles became a major port which allowed for growth and new industries.
The Folsom Powerhouse was built in 1895. Water from the American River was used to run generators. It allowed electricity to be transmitted 22 miles downstream to Sacramento. This was the farthest electricity had been transmitted at that time.
Wars helped create new industry in California. During WW I, airplanes were needed. California’s good weather made flying possible year round and you could build airplanes outside. California became the aircraft-manufacturing center of the world.
Movies are an industry as well. Movies were first filmed in New York, New Jersey and Chicago; but the warmth and beauty of Southern California attracted film-makers. Studios were built in Hollywood. WW I helped the movie business because people went to enjoy themselves and forget about the war. In the 1920s talking movies began. Movie stars grew rich and famous.
Movies led to the industry of tourism. Tourism is “traveling for pleasure”. Films drew visitors to California because people came to see the studios and the stars.
The Dust Bowl was a 50-million-acre region in the middle of the United States. It was caused by drought and winds. Many farms were destroyed. This took place during the Great Depression. The Great Depression was a time when many workers lost their jobs. Many people decided to come to California to start a new life. Most worked on farms but some helped build the Golden Gate Bridge in San Francisco. President Franklin Delano Roosevelt promised a New Deal which provided new jobs building railroads, canals and parks throughout the United States. This hard time in our country helped California grow.
On December 7, 1941, Japan attacked a United States military base at Pearl Harbor in Hawaii. California again played a big part in providing needed supplies for World War II. A large manufacturing industry grew. Manufacturing is the process of turning materials into finished products. An example is planes and ships being built from steel. Shipyards in San Francisco Bay made about 700 ships during the war. These ships were put together like a toy. Each part had a number. One numbered part was connected to the next. Before the war it took up to a year to build a ship. During the war it took three-and-a-half days.
The war also helped industries grow in California. After the war, all the old war planes were put into junkyards. A new age of aviation began. Aviation is the building and flying of airplanes. Three things helped this industry grow. First was the invention of the jet plane. Second were the many universities with scientists from around the world who helped created better airplane designs and more powerful engines. Third, California already had the manufacturing industries that began during the war.
Other industries grew out of the war as well. Better and faster planes created a desire to go into space. Rockets were created and the aerospace industry began. Aerospace was the new word that included spacecraft as well as airplanes.
Francis P. Shepard studied the waters off the coast of San Diego. He was the first American to explore the ocean floor in a deep-sea submarine. The submarine was designed by Jacques Cousteau and named the “Diving Saucer”.
There were also advancements in agriculture. The science and technology developed at California universities helped crops to stay healthy and helped to develop faster, better machines.
Following the war, people wanted a comfortable life. California had room to grow, beauty, warmth and high-paying jobs. Many people came to California for these things and California grew quickly. Thousands of new homes were built. These new housing areas were built outside major cities and were called suburbs. Schools, shopping centers and theaters were built. Soon houses began to replace many of the tree groves and farms that once existed. Freeways were built to connect these cities. The Pasadena Freeway was the state’s first freeway.
Activities
1. Fill in the blank worksheet
The war also helped industries grow in California. After the war, all the old war planes were put into junkyards. A new age of aviation began. Aviation is the building and flying of airplanes. Three things helped this industry grow. First was the invention of the jet plane. Second were the many universities with scientists from around the world who helped created better airplane designs and more powerful engines. Third, California already had the manufacturing industries that began during the war.
Other industries grew out of the war as well. Better and faster planes created a desire to go into space. Rockets were created and the aerospace industry began. Aerospace was the new word that included spacecraft as well as airplanes.
Francis P. Shepard studied the waters off the coast of San Diego. He was the first American to explore the ocean floor in a deep-sea submarine. The submarine was designed by Jacques Cousteau and named the “Diving Saucer”.
There were also advancements in agriculture. The science and technology developed at California universities helped crops to stay healthy and helped to develop faster, better machines.
Following the war, people wanted a comfortable life. California had room to grow, beauty, warmth and high-paying jobs. Many people came to California for these things and California grew quickly. Thousands of new homes were built. These new housing areas were built outside major cities and were called suburbs. Schools, shopping centers and theaters were built. Soon houses began to replace many of the tree groves and farms that once existed. Freeways were built to connect these cities. The Pasadena Freeway was the state’s first freeway.
Activities
1. Fill in the blank worksheet
| Link |
3. Paper Airplanes
Friday, August 10, 2018
California History Lesson 26 (New Cultures)
California History
New Cultures
Lesson 26
Immigrants are people who move to another country so that they can make a new home there. Sometimes they are looking for better jobs others need safety from wars or violence in their old countries. Because of the Gold Rush, many people thought of California as a place of wealth. Many also heard about the warm weather and rich farmland.
1. Identify countries where immigrants came from on a map: Ireland, Germany, Armenia, Portugal, France, Sweden, China, Japan, Philippines
2. On a map of California show where immigrants from these countries settled in California.
New Cultures
Lesson 26
Immigrants are people who move to another country so that they can make a new home there. Sometimes they are looking for better jobs others need safety from wars or violence in their old countries. Because of the Gold Rush, many people thought of California as a place of wealth. Many also heard about the warm weather and rich farmland.
Many immigrants came to the United States from Europe. They came from countries such as Ireland, Germany, Armenia, Portugal, France and Sweden. Often the immigrants from Europe settled on the east coast of the United States first. Immigrants were often treated unfairly and the few jobs they could find didn’t pay well; so these immigrants decided to come to California where they hoped to find the life they had been looking for when they first came to the United States.
Other immigrants crossed the Pacific from Asia. The first Asian immigrants came from China. They came for the Gold Rush but then helped build the Transcontinental Railroad. Later immigrants came from Japan and the Philippines.
Many of the immigrants who came to California were discriminated against. Discrimination is mistreating a group of people because of their appearance. The California Indians were forced onto reservations. Many died from lack of food and disease. Asian immigrants had to stop at Angel Island in San Francisco Bay. Many spent days, weeks and even a year or more waiting to see if they would be allowed into California. Even after all that time, many were sent back to their homeland.
Many of the immigrants who came to California were discriminated against. Discrimination is mistreating a group of people because of their appearance. The California Indians were forced onto reservations. Many died from lack of food and disease. Asian immigrants had to stop at Angel Island in San Francisco Bay. Many spent days, weeks and even a year or more waiting to see if they would be allowed into California. Even after all that time, many were sent back to their homeland.
The immigrants who came helped to change California. We can see their influence in our landmarks, important places, street names, foods and literature. The United States has been called a “melting pot” of different people. This means people from different countries and cultures have come together to live. They work together, learn from one another and create a place where everyone can share in the American Dream.
Activities
Activities
1. Identify countries where immigrants came from on a map: Ireland, Germany, Armenia, Portugal, France, Sweden, China, Japan, Philippines

2. On a map of California show where immigrants from these countries settled in California.
3. Match items we see in California with country from which they came.
4. German School Cone (I have kids make cones and then have a parent fill them while we're outside on break. I hand them out at the end of class.)
 |
| Link |
5. Chinese cherry blossom lantern or dragon
 |
| Link |
California History Lesson 25 (Agriculture)
California History
Agriculture
Lesson 25
What is agriculture? Growing crops and raising animals to provide food, wool and other products. “An easy way to remember what agriculture is: The Five Fs (Food, Fiber, Forests, Flowers, Fuel). Farmers and ranchers grow many different kinds of food - everything from the strawberries growing in fields to the hamburger on your dinner plate. Cotton from plants and wool from animals are types of textile fiber. Many products that we use every day are made from fiber. Trees from forests are used to make more than 5,000 products that we use everyday. Flowers are a big part of California agriculture. Cut flowers, fruit trees, nursery plants, and houseplants are all a part of agriculture. Fuel can be used to make energy. There are many uses for energy on the farm. Cow manure can be made into fuel that can heat or cool buildings, or provide lighting and electricity. Corn can be made into ethanol, which is used to fuel cars, trucks and tractors.
California was described as the richest, most beautiful, healthiest region in the world. Farming soon surpassed ranching and mining. Today California is the leading agricultural state in our country.
1. “There’s a Farm in my Pizza?” Discuss all the agriculture needed to make a pizza using p. 10 of California Agriculture: Farming is Everywhere Coloring Book. (Link)
2. Using “California Agriculture Production Regions” worksheet, match Production Areas with Major Commodities. Then color the map to match the color of the production area on the worksheet.
Agriculture
Lesson 25
What is agriculture? Growing crops and raising animals to provide food, wool and other products. “An easy way to remember what agriculture is: The Five Fs (Food, Fiber, Forests, Flowers, Fuel). Farmers and ranchers grow many different kinds of food - everything from the strawberries growing in fields to the hamburger on your dinner plate. Cotton from plants and wool from animals are types of textile fiber. Many products that we use every day are made from fiber. Trees from forests are used to make more than 5,000 products that we use everyday. Flowers are a big part of California agriculture. Cut flowers, fruit trees, nursery plants, and houseplants are all a part of agriculture. Fuel can be used to make energy. There are many uses for energy on the farm. Cow manure can be made into fuel that can heat or cool buildings, or provide lighting and electricity. Corn can be made into ethanol, which is used to fuel cars, trucks and tractors.
California was described as the richest, most beautiful, healthiest region in the world. Farming soon surpassed ranching and mining. Today California is the leading agricultural state in our country.
Sheep-raising became important as did raising dairy cows. The first crops grown in California were wheat and some cotton.
The farmers faced many problems. California has two seasons - wet and dry. They had to raise crops that would stand the high transportation costs to markets. It was hard to get land from the railroad company. And irrigation for crops was needed.
Today the San Joaquin Valley is one of the greatest agricultural regions, but at first it was considered a desert. It was in need of irrigation. Irrigation is the delivery of water to arid, dry land. When water was brought to the dry land the land became farmable. By 1890 one-fourth of all California farms were being irrigated. An old man told his son: “Plant your lands; these be your best gold fields, for all must eat while they live.”
California became a leading producer of apples, apricots, cherries, peaches, pears, plums and prunes. Today the state produces more than half of the world’s supply of raisins. Oranges have become an important crop in California as well as lemons. California grows more lemons than all the other states put together. Walnuts, almonds and macadamia nuts, grow well in California as well as olives, dates, figs and avocados.
Besides farming, there are also important minerals found in California. Besides gold, miners also have mined silver and borax. Borax is found in Death Valley. It is used for cleaning things, as a water softener and as a preservative. The Indians had used a black, sticky substance to line their baskets which allowed them to carry water without them leaking. This turned out to be petroleum - oil. The petroleum industry soon became a leading industry in California.
The lumber industry quickly grew in California. Crates were needed to ship oranges and lemons. Lumber was needed for mining, housing, railroad construction and shipbuilding. Other industries that grew are meatpacking, milling, processing of fruits and vegetables, manufacture of leather goods and textiles, blacksmithing and the processing of steel.
Activities
California became a leading producer of apples, apricots, cherries, peaches, pears, plums and prunes. Today the state produces more than half of the world’s supply of raisins. Oranges have become an important crop in California as well as lemons. California grows more lemons than all the other states put together. Walnuts, almonds and macadamia nuts, grow well in California as well as olives, dates, figs and avocados.
Besides farming, there are also important minerals found in California. Besides gold, miners also have mined silver and borax. Borax is found in Death Valley. It is used for cleaning things, as a water softener and as a preservative. The Indians had used a black, sticky substance to line their baskets which allowed them to carry water without them leaking. This turned out to be petroleum - oil. The petroleum industry soon became a leading industry in California.
The lumber industry quickly grew in California. Crates were needed to ship oranges and lemons. Lumber was needed for mining, housing, railroad construction and shipbuilding. Other industries that grew are meatpacking, milling, processing of fruits and vegetables, manufacture of leather goods and textiles, blacksmithing and the processing of steel.
Activities
1. “There’s a Farm in my Pizza?” Discuss all the agriculture needed to make a pizza using p. 10 of California Agriculture: Farming is Everywhere Coloring Book. (Link)
2. Using “California Agriculture Production Regions” worksheet, match Production Areas with Major Commodities. Then color the map to match the color of the production area on the worksheet.
3. The Five Fs activity (p. 9 of California Agriculture: Farming is Everywhere Coloring Book)
4. On the “Farming is Everywhere” map (p. 12 of California Agriculture: Farming is Everywhere Coloring Book), circle county you live in and name top crops
5. Fruit craft (Watermelon is easiest!)
4. On the “Farming is Everywhere” map (p. 12 of California Agriculture: Farming is Everywhere Coloring Book), circle county you live in and name top crops
5. Fruit craft (Watermelon is easiest!)
 |
| Link |
Wednesday, August 8, 2018
California History Lesson 24 (Transcontinental Railroad)
California History
Transcontinental Railroad
Lesson 24
The Pony Express was no longer needed after the invention of the telegraph. The transcontinental line was completed on October 24, 1861. Transcontinental means “across the continent”. Messages could be sent by Morse Code in a manner of minutes.
In 1848 an attempt was made to develop a steamship line which would carry mail from Panama to California through the Isthmus of Panama. There was difficulty crossing Panama to the Pacific. Carriers had to travel primitive trails, go upstream in long canoes, endure mosquitoes, bad water and disease. A railroad was needed. In 1850, work began on a railroad across South America. It took 5 years of hard work. This was the first transcontinental railroad in the Western Hemisphere.
Californians desired to have a railroad that crossed the continent. It would take large amounts of money and lots of work. In 1862 when the south seceded from the Union, Congress passed the Pacific Railroad Act. Four wealthy men formed the Central Pacific Railroad Company. They became known as the Big Four. The Pacific Railroad Act named the Central Pacific and the Union Pacific Railroad Companies to build the railway. The Central Pacific Railroad was to build east from Sacramento. The Union Pacific Railroad was to build west from Omaha, Nebraska. Work began in 1863 in Sacramento. The Union Pacific began its work in the summer of 1865. Many Chinese men were hired to work on the railroad because they would work for low wages. The work was hard and dangerous. The summit of the Sierra was reached in 1867. Track was laid at the rate of between two and six miles a day by each company. Competition between the railroad companies increased the closer they got to one another. After seven years, in May of 1869, the two lines met at Promontory Point in Utah. They laid a total of 2,221 miles of track. People could travel from the Atlantic states to California in just five days. California was now linked with the eastern United States.
1) Chart showing number of days it took to travel each route.
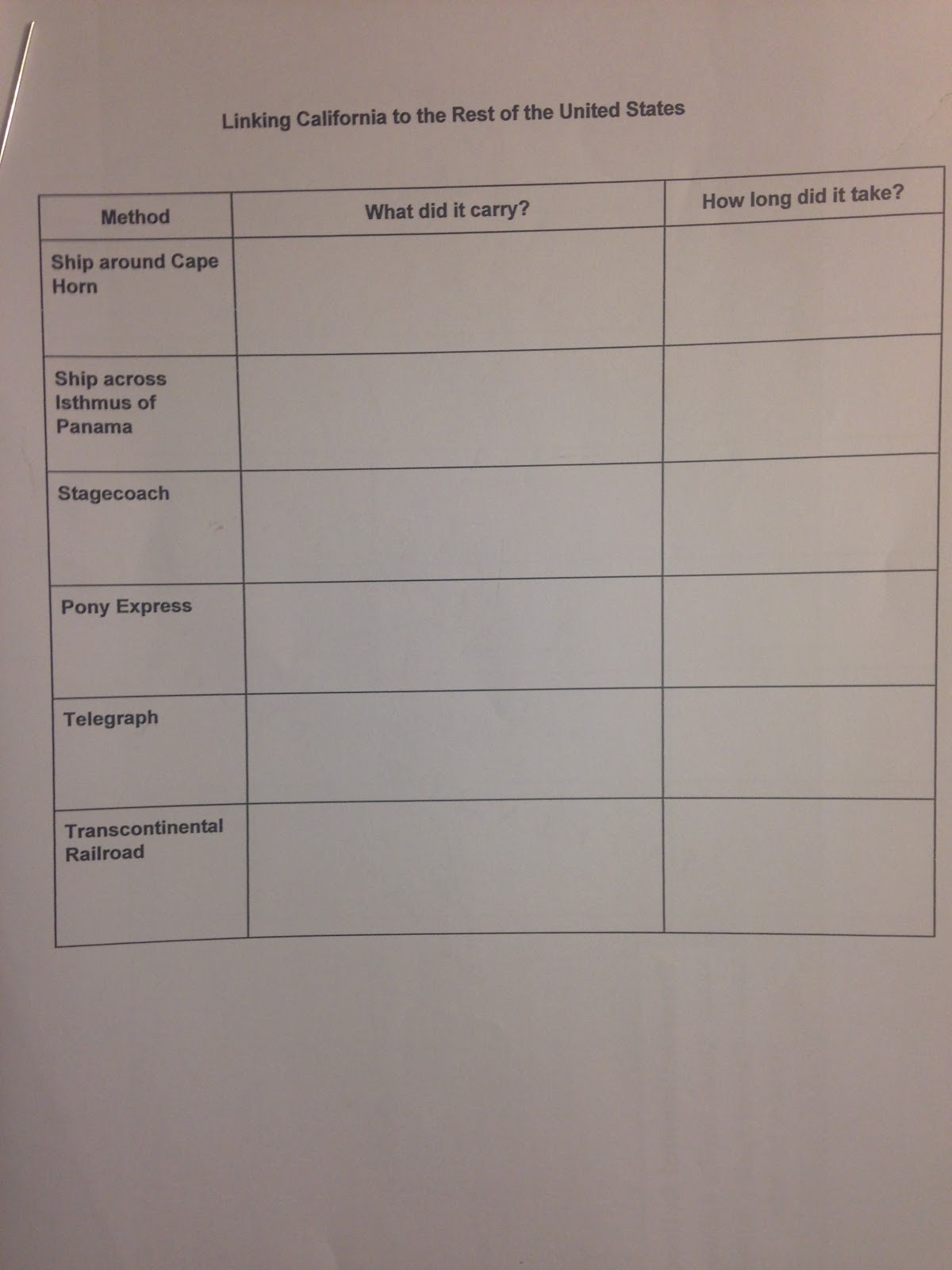
2) Map showing the Transcontinental Railroad. Trace each route with a different color.

3) Candy train
Transcontinental Railroad
Lesson 24
The Pony Express was no longer needed after the invention of the telegraph. The transcontinental line was completed on October 24, 1861. Transcontinental means “across the continent”. Messages could be sent by Morse Code in a manner of minutes.
In 1848 an attempt was made to develop a steamship line which would carry mail from Panama to California through the Isthmus of Panama. There was difficulty crossing Panama to the Pacific. Carriers had to travel primitive trails, go upstream in long canoes, endure mosquitoes, bad water and disease. A railroad was needed. In 1850, work began on a railroad across South America. It took 5 years of hard work. This was the first transcontinental railroad in the Western Hemisphere.
Californians desired to have a railroad that crossed the continent. It would take large amounts of money and lots of work. In 1862 when the south seceded from the Union, Congress passed the Pacific Railroad Act. Four wealthy men formed the Central Pacific Railroad Company. They became known as the Big Four. The Pacific Railroad Act named the Central Pacific and the Union Pacific Railroad Companies to build the railway. The Central Pacific Railroad was to build east from Sacramento. The Union Pacific Railroad was to build west from Omaha, Nebraska. Work began in 1863 in Sacramento. The Union Pacific began its work in the summer of 1865. Many Chinese men were hired to work on the railroad because they would work for low wages. The work was hard and dangerous. The summit of the Sierra was reached in 1867. Track was laid at the rate of between two and six miles a day by each company. Competition between the railroad companies increased the closer they got to one another. After seven years, in May of 1869, the two lines met at Promontory Point in Utah. They laid a total of 2,221 miles of track. People could travel from the Atlantic states to California in just five days. California was now linked with the eastern United States.
1) Chart showing number of days it took to travel each route.
2) Map showing the Transcontinental Railroad. Trace each route with a different color.
3) Candy train
| Link |
California History Lesson 23 (Pony Express)
California History
Pony Express
Lesson 23
Sea travel played an important part of California’s history. Ships carried on the fur, hide and tallow and otter trade. During the Gold Rush, many people wanting to travel to California came by ship from New York to San Francisco. They either sailed around Cape Horn at the tip of South America or across the Isthmus of Panama in Central America. Traveling around Cape Horn took 6-8 months. Traveling through the Isthmus of Panama took 2-3 months.
Soon stagecoach companies formed. The first large stagecoach company was Adams and Company. They carried mail, gold and cash from the Sierras to New England. Their rival was Wells Fargo. It worked with the Pacific Mail Steamship Company and could handle goods sent to the Atlantic states via the Isthmus of Panama. Its lines covered every part of the state. In 1857, John Butterfield set up a stage route with way stations where travelers could eat and horses could be exchanged. Travelers could go from St. Louis, Missouri to San Francisco, California in 3-5 months. The stagecoaches also carried mail and goods. During the War Between the States, when the nation was divided, the Butterfield stage line ended.
People desired mail to get from one place to another more quickly. The Pony Express was created by William H. Russell in 1860 for this purpose. This mail system went from Saint Louis to Sacramento which was a distance of 1,980 miles. There were 200 stations, 500 horses and 80 riders. Riders would only spend two minutes at each station transferring the mail pouch and saddle to a fresh horse. Riders could travel the distance in just 10 days. It cost $5 for each ½ ounce to send a letter across the continent. Later the price dropped to $1.
Activities
1) Pony Express Timeline
1.William H. Russell, Alexander Majors, and William B. Waddell introduced the Pony Express as a way to deliver mail from St. Joseph, Missouri, to Sacramento, California. They promised delivery in 10 days at a cost of $5 per half ounce.
2. They secured about 420 high-grade ponies and about 80 male riders. Russell and his men also hired 400 station men and women. One hundred and ninety stations were opened 15-25 miles apart.
3. The riders would race at a top speed of about 10 miles per hour from one “relay station” to the next where they would make two-minute switches to fresh horses and continue on. Specifically designed mail-filled saddlebags called mochilas were easily transferred from one horse to another.
4. The first riders departed on April 3, 1860. Though the trips were rough, the mail arrived ten days later and great celebrations took place.
5. The most famous Pony Express rider was William F. Cody, better known as Buffalo Bill. He made one 384-mile trip without stopping for a sleep break!
6. Rider Bob Haslam, known as “Pony Bob,” pushed his speed to an incredible 15 miles per hour, doing his part to deliver President Abraham Lincoln’s inaugural address to California. The whole trip was made in seven days and 17 hours.
7. In November of 1861, the Pony Express made its final delivery. In a total of 308 runs, riders had traveled 616,000 miles and delivered 34,753 pieces of mail. The entire time, only one mochila was lost.
Used pictures from an activity in U.S. History Little Books Famous Events, Teacher Created Materials, Inc.

2) Design a stamp
Pony Express
Lesson 23
Sea travel played an important part of California’s history. Ships carried on the fur, hide and tallow and otter trade. During the Gold Rush, many people wanting to travel to California came by ship from New York to San Francisco. They either sailed around Cape Horn at the tip of South America or across the Isthmus of Panama in Central America. Traveling around Cape Horn took 6-8 months. Traveling through the Isthmus of Panama took 2-3 months.
Soon stagecoach companies formed. The first large stagecoach company was Adams and Company. They carried mail, gold and cash from the Sierras to New England. Their rival was Wells Fargo. It worked with the Pacific Mail Steamship Company and could handle goods sent to the Atlantic states via the Isthmus of Panama. Its lines covered every part of the state. In 1857, John Butterfield set up a stage route with way stations where travelers could eat and horses could be exchanged. Travelers could go from St. Louis, Missouri to San Francisco, California in 3-5 months. The stagecoaches also carried mail and goods. During the War Between the States, when the nation was divided, the Butterfield stage line ended.
People desired mail to get from one place to another more quickly. The Pony Express was created by William H. Russell in 1860 for this purpose. This mail system went from Saint Louis to Sacramento which was a distance of 1,980 miles. There were 200 stations, 500 horses and 80 riders. Riders would only spend two minutes at each station transferring the mail pouch and saddle to a fresh horse. Riders could travel the distance in just 10 days. It cost $5 for each ½ ounce to send a letter across the continent. Later the price dropped to $1.
Activities
1) Pony Express Timeline
1.William H. Russell, Alexander Majors, and William B. Waddell introduced the Pony Express as a way to deliver mail from St. Joseph, Missouri, to Sacramento, California. They promised delivery in 10 days at a cost of $5 per half ounce.
2. They secured about 420 high-grade ponies and about 80 male riders. Russell and his men also hired 400 station men and women. One hundred and ninety stations were opened 15-25 miles apart.
3. The riders would race at a top speed of about 10 miles per hour from one “relay station” to the next where they would make two-minute switches to fresh horses and continue on. Specifically designed mail-filled saddlebags called mochilas were easily transferred from one horse to another.
4. The first riders departed on April 3, 1860. Though the trips were rough, the mail arrived ten days later and great celebrations took place.
5. The most famous Pony Express rider was William F. Cody, better known as Buffalo Bill. He made one 384-mile trip without stopping for a sleep break!
6. Rider Bob Haslam, known as “Pony Bob,” pushed his speed to an incredible 15 miles per hour, doing his part to deliver President Abraham Lincoln’s inaugural address to California. The whole trip was made in seven days and 17 hours.
7. In November of 1861, the Pony Express made its final delivery. In a total of 308 runs, riders had traveled 616,000 miles and delivered 34,753 pieces of mail. The entire time, only one mochila was lost.
Used pictures from an activity in U.S. History Little Books Famous Events, Teacher Created Materials, Inc.
2) Design a stamp
| Link |
California History Lesson 22 (Statehood)
California History
Statehood
Lesson 22
The first inhabitants of California were the Native Americans. Then the Spaniards came who set up missions and presidios. Mexico got tired of the lack of support they received from Spain, so they went to war and won their independence. California was then owned by Mexico. Ranchos replaced the missions. The United States became interested in California as more and more people began to move west. The United States went to war with Mexico. For the sum of fifteen million dollars, the United States took possession of California, Texas and all the land in between.
The Gold Rush brought many people to California. It was hard to govern so many people. Representatives from every part of California were called together to write a constitution. A constitution is a set of laws for people to live by. Forty-eight delegates me on September 1, 1849. The delegation decided they wanted California to be a state, that no slavery would be allowed in California, white and Native American males were given the right to vote, and the boundaries they agreed on are the boundaries we have today. Once this constitution was approved by the voters, it was sent to Washington D.C. and presented to Congress. On September 9, 1850, President Zachary Taylor signed the bill for the admission of California to the United States, making California the 31st state.
Each state has a seal to represent it. California’s seal was adopted at the Constitutional Convention of 1849. Each symbol on the state represents a part of California’s history.

1) The 31 stars represent the number of states in the Union at that time.
2) Eureka means “I found it!” as a reminder of the gold found in the state.
3) The peaks of the Sierra Nevada stand for the grandeur of the nature.
4) Ships on the Sacramento River stand for the commerce (buying and selling goods) of the state
5) A miner laboring with a pick, rocker and pan represents industry (making goods from raw materials).
6) Agricultural wealth is seen in a sheaf of wheat and a cluster of grapes.
7) The armored figure of Minerva, the goddess of arts, sciences, wisdom and war in ancient Greek mythology keeps watch over the state.
8) According to myth, Minerva was born full-grown, just as California came into the Union without having first been a territory.
9) At her feet a grizzly bear symbolizes the state of California.
Activities
Statehood
Lesson 22
The first inhabitants of California were the Native Americans. Then the Spaniards came who set up missions and presidios. Mexico got tired of the lack of support they received from Spain, so they went to war and won their independence. California was then owned by Mexico. Ranchos replaced the missions. The United States became interested in California as more and more people began to move west. The United States went to war with Mexico. For the sum of fifteen million dollars, the United States took possession of California, Texas and all the land in between.
The Gold Rush brought many people to California. It was hard to govern so many people. Representatives from every part of California were called together to write a constitution. A constitution is a set of laws for people to live by. Forty-eight delegates me on September 1, 1849. The delegation decided they wanted California to be a state, that no slavery would be allowed in California, white and Native American males were given the right to vote, and the boundaries they agreed on are the boundaries we have today. Once this constitution was approved by the voters, it was sent to Washington D.C. and presented to Congress. On September 9, 1850, President Zachary Taylor signed the bill for the admission of California to the United States, making California the 31st state.
Each state has a seal to represent it. California’s seal was adopted at the Constitutional Convention of 1849. Each symbol on the state represents a part of California’s history.

1) The 31 stars represent the number of states in the Union at that time.
2) Eureka means “I found it!” as a reminder of the gold found in the state.
3) The peaks of the Sierra Nevada stand for the grandeur of the nature.
4) Ships on the Sacramento River stand for the commerce (buying and selling goods) of the state
5) A miner laboring with a pick, rocker and pan represents industry (making goods from raw materials).
6) Agricultural wealth is seen in a sheaf of wheat and a cluster of grapes.
7) The armored figure of Minerva, the goddess of arts, sciences, wisdom and war in ancient Greek mythology keeps watch over the state.
8) According to myth, Minerva was born full-grown, just as California came into the Union without having first been a territory.
9) At her feet a grizzly bear symbolizes the state of California.
Activities
3) Dot to Dot
 |
| Link |
4) Timeline Movie: 1) Native Americans 2) Missions 3) Ranchos 4) Pioneers 5) Bear Flag Revolt 6) Gold Rush 7) Statehood
Monday, August 6, 2018
California History Lesson 21 (Gold Rush)
California History
Gold Rush
Lesson 21
Activities:
1. "Maps Tell the Story of the Mother Lode"
2. "As Good As Gold" Crossword
 |
| Created on TheTeachersCorner.net Crossword Maker |
3. Gold Rush Word search
 |
| Link |
4. Pop-up Miner picture
 |
| Link |
California History Lesson 20 (Gold Rush)
California History
Gold Rush
Lesson 20
The Gold Rush
Gold was discovered in California just 90 days before the end of the war with Mexico. The discovery of gold brought a lot of attention to California. John Sutter was the man who took care of all the immigrants coming into California. He needed lumber to build items to help the travelers. John Marshall was hired to find a place for a sawmill. He found a good place on the American River. It was there that he first found gold. They tried to keep it a secret because John Sutter needed the men to do their work. If word got out about gold, his workers would be distracted. Sadly, news spread fast with the help of Sam Brannan. He knew that men would need supplies in order to keep up their stakes and thought he could get rich selling them the things they would need. So he went out into the streets of San Francisco shouting that gold had been found in the American River.
Gold fever struck and people left everything to search for gold. Letters were sent home to the east and the governor of California sent a report back to Washington D.C. After President Polk confirmed the rumors of gold in California, the Gold Rush began. People were called forty-niners because they began searching for gold in 1849. They came by land routes from every state in the Union, by sea around the Horn of South America and through the isthmus at Panama, and many came from Mexico as well. The fastest route to the gold field was around the Isthmus of Panama. It took 2-3 months. The longest route was around Cape Horn which took 6-8 months. The cheapest way to get to the gold fields was the overland route which took 3-5 months. Among the people who came to California hunting for gold were African Americans, Mexicans and the Chinese. About 1,000 African Americans came to California to search for gold. Some were free, but others were offered their freedom if they found $2,000 in gold. 1 in 4 miners were Chinese. Not many women joined the Gold Rush because it was too expensive to travel to California.
To begin searching for gold, a person first had to make a claim. He would use stakes to mark the boundaries of his claim. The gold that was first found in the American River was placer gold which means gold that is easily found on the earth’s surface. In the beginning, men panned for gold by scooping up some dirt from the riverbed and swirling it around in a flat-bottom pan. The gold settled on the bottom while the dirt washed out. This was the easiest way to look for gold. And the easiest place to find gold was along the rivers of the Sierra Nevada Mountains. Later a rocker or cradle was built. Dirt was shoveled into it and water washed over it. Two men would work together to shake the cradle. The lighter gravel and muddy water fell through and the heavier pieces, like gold stayed behind. From this design, a Long Tom was created. 5-10 men would work a long trough that used fast moving water to sift through shovelfuls of gravel. The Mexican miners were skilled at dry digging along the mountains. The area where the largest amount of gold was found was called the “Mother Lode.” After several years, most of the gold had been mined from the rivers. Hydraulic mining began. This was where huge hoses were used to spray water against riverbank. The first of the gold found was called placer gold which means gold that is easily found on the earth’s surface.
Life in the gold camps was not easy. Most men did not have proper food or clothing. They stood in very cold water for long hours. Many became ill. Goods were very expensive. There was a lot of theft. Men entertained themselves by playing cards and watching bear fights and traveling entertainers. Sundays were a day of rest for the miners. On this day the men would wash their clothes and do their chores.
Some gold seekers made a fortune in gold, but many did not. Even men who found gold ended up poor because the cost of food and supplies was so high. The best way to become rich during the Gold Rush was to be a merchant, like Sam Brannan. Levi Strauss is another example. He became rich by creating denim pants for the forty-niners to wear. Because of the difficulties, the forty-niners left the mines by the mid-1850’s. Many returned home; but many stayed in California and helped it to grow. In fact, over 500 ships were abandoned in the San Francisco harbor because men left their jobs and went looking for gold. But San Francisco used the wood from the ships to build shops, hotels and warehouses. Many entrepreneurs set up new, independent businesses to help California grow.
Activities
1)Routes by Sea Map - Trace the three different routes with colored pencill
 2)Gold Rush Bingo (Link)
2)Gold Rush Bingo (Link)
1)Routes by Sea Map - Trace the three different routes with colored pencill
3) Create a Gold Rush map
| Link |
Or Put together a picture frame with popsicle sticks and rocks. Draw a picture for the frame.
| Link |
California History Lesson 19 (Bear Flag Revolt)
California History
Bear Flag Revolt
Lesson 19
The United States wanted to expand from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean. This was known as Manifest Destiny. This meant the United States needed to gain control of California. Mexico, however, refused to sell California to the United States. The economy of Mexican California was very weak. Only some of the landowners wanted Mexico to rule California. The Mexican government did not have the money to pay soldiers in California. Squatters who lived on California land without permission were afraid that the Mexican leader would attack them and make them leave. When James K. Polk became President, he sent Thomas O. Larkin to stir up the natives to revolt against Mexican rule. After tensions rose, John C. Fremont, with the support of President Polk, set out to attack an old fort in Sonoma. He had seen that California was not well defended and hoped to get control of California. American settlers rebelled and created the Bear Flag Republic. Those who marched into Sonoma called themselves Osos which is the Spanish word for “bear”. The Mexican general there was ready for the quarrels between the Californios and American settlers to end. He willingly surrendered; allowing papers to be drawn up and signed and himself to be taken into custody at Sutter’s Fort. The California Republic was born. This was to be known as the Bear Flag Revolt.
Fremont continued south to capture Monterey and Santa Barbara. A flag was raised in Monterey and then the ports of San Francisco, San Diego and Los Angeles were seized. The Californios rose up and forced out the American army from Los Angeles; but later it was recaptured by U.S. forces. The United States had declared war on Mexico on May 13, 1846. The Mexican-American War ended with the signing of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo on February 3, 1848. The United States paid Mexico $15,000,000 and kept Texas, California and all the land in between. The Californios became citizens of the United States and were allowed to keep their land. The first Governor of California was General Kearny who had helped defeat Mexico. Nine days earlier, gold had been found in the Sierra Nevada mountains. Neither Spain nor Mexico had discovered any. The history of California might have been different if they had.
Activities:
1) True - False Statements Worksheet
Bear Flag Republic and Mexican-American War True or False Statements
1. Many people felt that the United States should expand to reach from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean. This idea became known as Manifest Destiny. _________________
2. Mexico refused to sell California to the United States. _________________
3. The economy of Mexican California was very strong _________________
4. All the landowners wanted Mexico to rule California. _________________
5. The government in Mexico City did not have the money to pay soldiers in California. _________________
6. During his first expedition to the West, John C. Fremont noticed that California was well defended. _________________
7. John Fremont hoped to take control of California. _________________
8. Squatters who lived on California land without permission worried that California’s Mexican military leader, Jose Castro, would attack and make them leave. _________________
9. American settlers rebelled and created the Bear Flag Republic. _________________
10. The 30 settlers who marched into the town of Sonoma on June 14, 1846 called themselves the Osos. Oso is the Spanish word meaning “bear”. _________________
11. The Bear Flag Revolt began in Sacramento. _________________
12. The United States declared war on Mexico on May 13, 1846. _________________
13. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo officially ended the Mexican-American War. _________________
14. After the Mexican-American War the Californios became citizens of the United States of America and could keep the land they had owned before the war. _________________
2) Shade states acquired from Mexico by the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo on a map.
3) Make own Bear Flag
White construction paper
Stencils
Red paint
Filler Activities:
Bear Flag Dot-to-Dot
 |
| Link |
California History Lesson 18 (Pioneers)
California History
Pioneers
Lesson 18
During Spanish and Mexican rule, American ships from the east began coming to the coast of California to hunt for otter pelts. Some participated in the hide and tallow trade during Mexican rule. This let others know that California was a place to be desired.
Lewis and Clark were sent to explore the Northwest United States. They had a French guide, Charbonnean, and his Indian wife, Sacajawea. They shared the Gospel with the Indians they met. Following the report made by Lewis and Clark, Jedediah Smith, who was a beaver hunter, set out on a land expedition. He crossed the Colorado River, the Mojave Desert, and the San Bernardino Mountains. Smith was a strong Christian and he carried his Bible with him wherever he went. He was eventually killed by Comanches on the Santa Fe Trail.
Joseph Reddeford Walker was a fur trapper from Tennessee and Missouri. He made the first westward crossing through the Sierra Nevada. He was followed by Joseph Chapman, Abel Stearns and Thomas Larkin. Abel Stearns and Thomas Larkin were accepted by the Mexican government and given land. The first American woman to live in California was Rachel Hobson Holmes.
John Marsh came in one of the first overland groups. He was a doctor who had the first successful rancho in the Central Valley near Sacramento. Two years after John Marsh came, John Sutter arrived and also settled along the Sacramento River.
Activities
1) Map showing overland routes
3) Yarn Dolls
| Link |
4) Covered Wagon and Horses
| Link |
| Link |
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)















